Responsible AI Deployment: Ensuring Robust Governance and Data Protection Controls
To better understand how DIFC-based firms are approaching AI deployment, the Dubai Financial Services Authority (‘DFSA’) conducted its first AI survey in 2024, followed by a more detailed assessment in 2025. The DFSA Artificial Intelligence Survey 2025 results reveal a significant surge in AI adoption across the DIFC, reflecting both growing confidence in AI technologies and the strategic value they create for firms.
Insights from the Survey
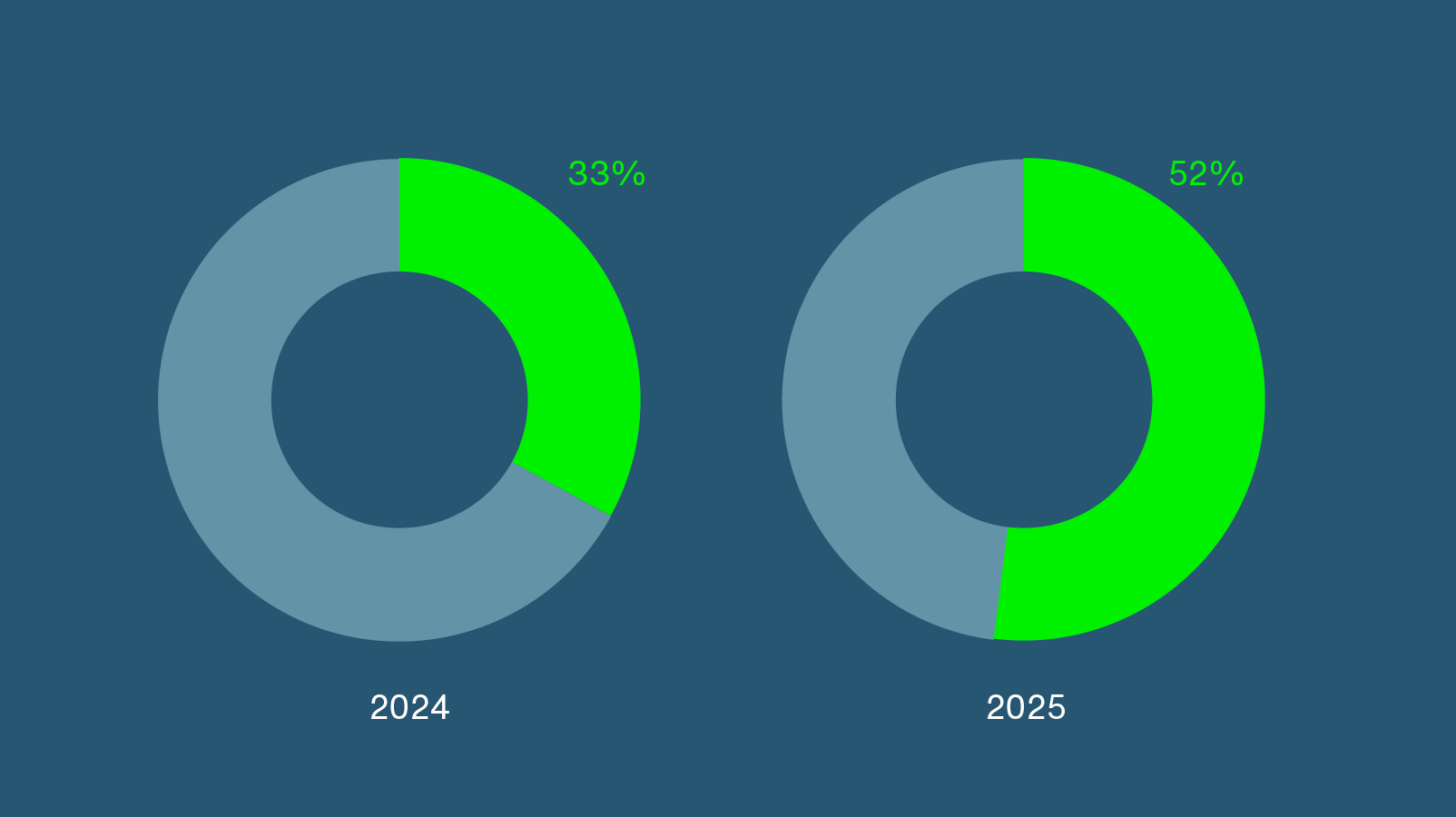
AI usage across the DIFC increased significantly, rising from 33% of firms in 2024 to 52% in 2025.
Generative AI recorded the most dramatic growth, increasing by 166%, followed by notable rises in narrow AI at 99%, while machine learning and deep learning applications each saw usage rise by more than 60%. Despite these developments, firms continue to cite regulatory uncertainty, cybersecurity risks, and implementation costs as the principal challenges to broader adoption. This suggests that, although AI usage is expanding, the underlying core barriers have remained largely consistent year over year.
A key observation is the shift in how deeply AI is being integrated into business functions. The number of firms using AI across a substantial part of their operations tripled, while those identifying AI as critical to at least one business area nearly doubled. Consistent with trends observed by other international financial services regulators, most AI deployments remain focus on internal functions such as HR, finance, legal, audit, compliance, and risk, reflecting a cautious approach to customer-facing applications. Nonetheless, expectations for future growth remain strong:

60% of firms anticipate increasing their AI usage within the next year, and 75% over the next three years.
Another area of concern is the increasing reliance on third-party developers and global cloud infrastructure. Sixty percent of firms operate over 90% of their AI systems on cloud platforms, with most depending on a small number of major providers such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure. This level of concentration introduces potential systemic risk, as disruptions at a single provider could impact numerous firms simultaneously. Strengthening third-party risk management and ensuring resilient cloud strategies are therefore essential.
The survey also reveals progress in AI governance, with 70% of firms reporting formal governance frameworks overseeing the use of AI. Nearly half of respondents stated they have a dedicated organisational AI policy, while others rely on existing governance and risk management frameworks and nearly 90% have allocated responsibility for AI oversight. However, significant gaps remain:
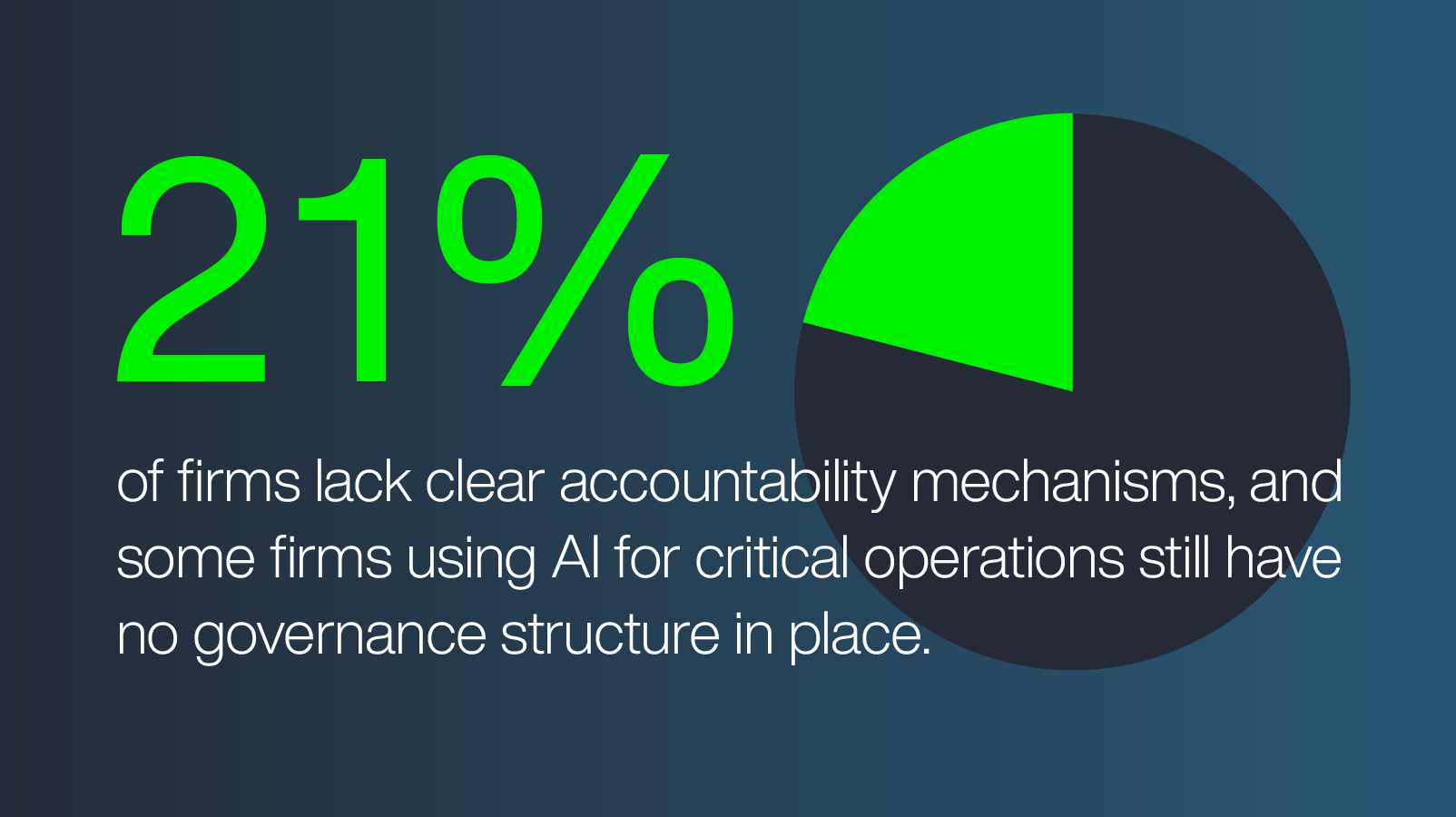
21% of firms lack clear accountability mechanisms, and some firms using AI for critical operations still have no governance structure in place.
What DIFC Firms Should Do:
Key AI Governance Measures
As AI adoption accelerates, DIFC firms must strengthen their governance, risk management, and compliance processes to ensure responsible deployment.
The weaknesses in AI governance pose heightened risks where AI systems process personal data, bringing compliance with the DIFC Data Protection Law 2020 (‘DPL’) and Regulation 10 of the DIFC Data Protection Regulations (‘Regulation 10’) pertaining to the use of AI systems into sharp focus.
To support compliance with regulatory expectations, firms should consider taking the following steps:
- develop a formal AI Governance Policy outlining ethical principles, approved use cases, transparency expectations, risk-management requirements, and escalation procedures
- designate a responsible individual or committee such as an Autonomous Systems Officer (‘ASO’) where required under Regulation 10, or an AI Oversight Committee to ensure clear accountability for AI risks and compliance
- conduct regular AI monitoring and model oversight, including testing for accuracy, fairness, bias, explainability, robustness, and performance drift throughout the AI lifecycle
- ensure strong data-protection compliance when AI systems process personal data, by adhering to the DIFC DPL and Regulation 10 principles such as lawful processing, fairness, transparency, security, and accountability
- carry out Data Protection Impact Assessments (‘DPIAs’) and AI-specific impact assessments before deploying systems that involve personal data or automated decision-making
- ensure privacy safeguards are implemented such as disabling any model-improvement training on customer data, seeking consent of users where appropriate, and implementing human intervention triggers as required under Regulation 10
- provide transparency notices explaining the human-defined purposes, principles, and limits governing the processing of personal data, outputs generated by the AI systems, underlying principles of the AI system’s development and design etc.
- strengthen third-party risk management by conducting thorough due diligence, implementing robust data protection and AI-specific contractual clauses (including restrictions on data use, requirements for transparency around AI model training, data minimisation, and prohibitions on secondary use), and ensuring ongoing vendor monitoring
- maintain an AI Register as required under Regulation 10, along with comprehensive documentation covering training-data sources, model-development processes, versioning, performance evaluations, and governance decisions, to support both internal accountability and regulatory supervisory review
- align with international AI governance standards, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology (‘NIST’) AI Risk Management Framework, Organisation for Economic Co‑operation and Development (‘OECD’) AI Principles, and ISO/IEC 42001:2023 – Artificial Intelligence Management System (‘AIMS’), to enhance transparency, accountability, and risk mitigation.
The DFSA has reaffirmed its commitment to a proportionate, risk-based approach that supports responsible innovation without stifling growth. As the financial sector increasingly integrates AI into core operations, firms that proactively enhance their governance frameworks, data-management practices, and oversight mechanisms will be best positioned to benefit from AI safely and sustainably. The rapid adoption of AI across the DIFC marks a promising step forward provided it is matched by robust, transparent, and accountable governance structures.
How Waystone Can Help?
Waystone has a dedicated Data Protection team with deep expertise in the DIFC and ADGM regulatory requirements. Our data protection specialists can support firms in meeting their Regulation 10 and broader AI-related obligations through a range of tailored services. This includes conducting AI-specific DPIAs, performing compliance assessments against Regulation 10, and the DIFC Data Protection Law 2020. We also assist with the development and maintenance of required documentation, such as AI registers, drafting transparency notices, privacy statements, and AI-related user disclosures to ensure clear communication with data subjects. We also offer ongoing advisory support to help firms strengthen their AI governance arrangements and establish effective data protection mechanisms.
For further details, please contact our Middle East Compliance Solutions Team.